Introduction
As Data Engineering evolves, so do the tools we use to manage and streamline our data workflows. Commercial Open-Source Pentaho Data Integration (PDI), commonly known as Kettle or Spoon, has been a popular choice for over a decade for many Data professionals. Hitachi Vantara acquired and continued to support Pentaho Community Edition along with the Commercial offering not just for the PDI / Data Integration platform but also the complete Business intelligence Suite which included a comprehensive set of tools with great flexibility, extensibility and hence used to be featured highly in the Analysts reports including Gartner BI Magic Quadrant, Forrester and Dresner’s Wisdom of Crowds.
Over the last few years, however, there has been a shift in industry and several niche Pentaho alternatives have appeared. Also, an alternative is needed for the Pentaho Community Edition users since Hitachi Vantara / Pentaho has stopped releasing or supporting the Community Edition (CE) of Pentaho Business Intelligence and Data Integration platforms since November of 2022. With the emergence of Apache Hop (Hop Orchestration Platform), a top-level Apache Open-Source Project, organizations now have a modern, flexible alternative that builds on the foundations laid by PDI and it is one of the top Pentaho Data Integration alternatives.
This is the first part of a series of articles where we try to highlight why Apache Hop can be considered as a replacement for the Pentaho Data Integration platform as we explore its benefits and also list a few of its limitations currently. In the next part, we provide a step-by-step guide to make the transition as smooth as possible.
Current Pentaho Enterprise and Community edition Releases:
A summary of the Release dates for the recent versions of Pentaho Platform along with their support commitment is captured in this table. You will notice that the last CE version was released in Nov 2022 while 3 newer EE versions have been released since.
Enterprise Version | Release Date | Community Version | Release Date | Support |
Pentaho 10.2 | Expected in Q3 2024 | NA | NA | Long Term |
Pentaho 10.1 GA | March 5, 2024 | NA | NA | Normal |
Pentaho 10.0 | December 01, 2023 | NA | NA | Limited |
Pentaho 9.5 | May 31, 2023 | NA | NA | Limited |
Pentaho 9.4 | November 01, 2022 | 9.4CE | Same as EE | Limited |
Pentaho 9.3 | May 04, 2022 | 9.3CE | Same as EE | Long Term |
Pentaho 9.2 | August 03, 2021 | 9.2CE | Same as EE | Unsupported |
Pentaho 9.1 | October 06, 2020 | NA | Unsupported | |
Pentaho 9.0 | February 04, 2020 | NA | Unsupported | |
Pentaho 8.3 | July 01, 2019 | 8.3CE | Same as EE | Unsupported |
Additionally, Pentaho EE 8.2, 8.1, 8.0 and Pentaho 7.X are all unsupported versions on date.
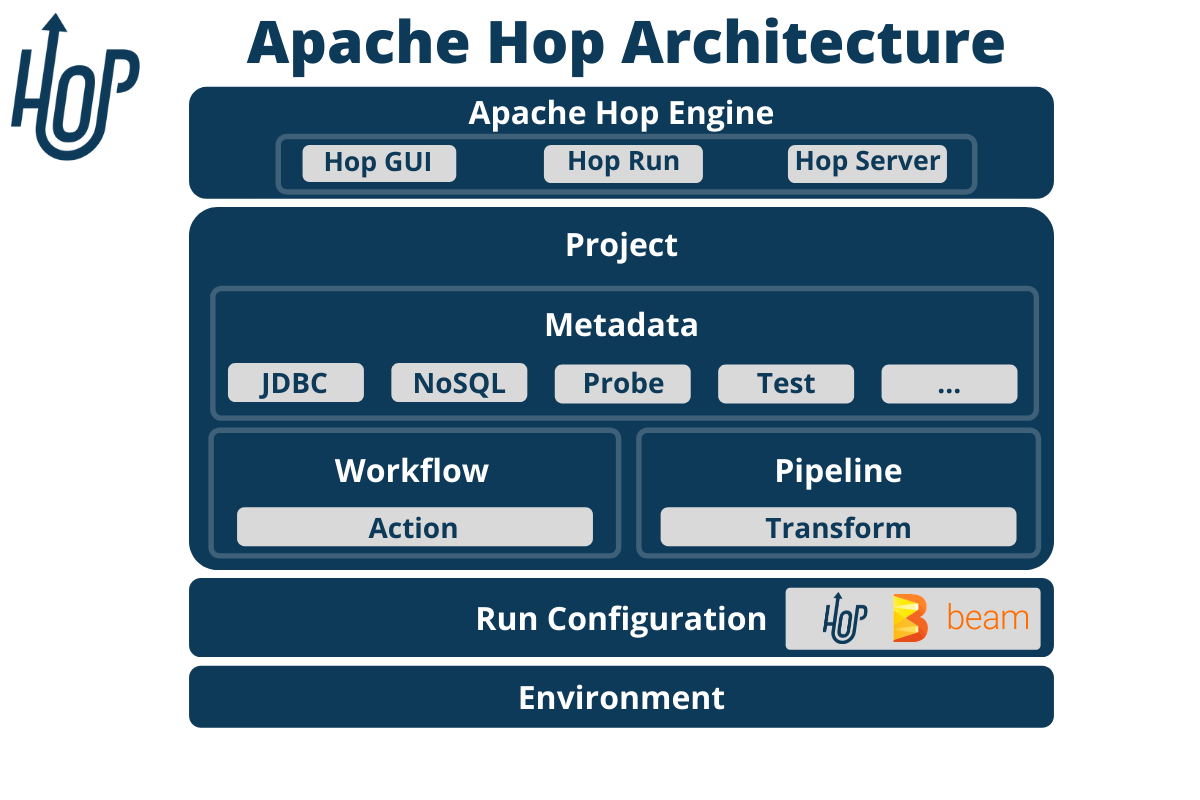
Apache HOP - An Overview
Apache HOP is an open-source data integration and orchestration platform.
It allows users to design, manage, and execute data workflows (pipelines) and integration tasks (workflows) with ease. HOP’s visual interface, combined with its powerful backend, simplifies complex data processes, making it accessible for both technical and non-technical users.
Evolution from Kettle to HOP
As the visionary behind both Pentaho Data Integration (Kettle) and Apache HOP (Hop Orchestration Platform), Matt Casters has played a pivotal role in shaping the tools that power modern data workflows.
The Early Days: Creating Kettle
Matt Casters began his journey into the world of data integration in the early 2000s. Frustrated by the lack of flexible and user-friendly ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools available at the time, he set out to create a solution that would simplify the complex processes of data integration. This led to the birth of Kettle, an acronym for “Kettle ETTL Environment” (where ETTL stands for Extraction, Transformation, Transportation, and Loading).
Key Features of Kettle:
- Visual Interface: Kettle introduced a visual drag-and-drop interface, making it accessible to users without extensive programming knowledge.
- Extensibility: It was designed to be highly extensible, allowing users to create custom plugins and transformations.
- Open Source: Recognizing the power of community collaboration, Matt released Kettle as an open-source project, inviting developers worldwide to contribute and improve the tool.
Kettle quickly gained popularity for its ease of use, flexibility, and robust capabilities. It became a cornerstone for data integration tasks, helping organizations manage and transform their data with unprecedented ease.
The Pentaho Era
In 2006, Matt Casters joined Pentaho, a company dedicated to providing open-source business intelligence (BI) solutions. Kettle was rebranded as Pentaho Data Integration (PDI) and integrated into the broader Pentaho suite. This move brought several advantages:
- Resource Support: Being part of Pentaho provided Kettle with added resources, including development support, marketing, and a broader user base.
- Enhanced Features: Under Pentaho, PDI saw many enhancements, including improved scalability, performance, and integration with other BI tools.
- Community Growth: The backing of Pentaho helped grow the community of users and contributors, driving further innovation and adoption.
Despite these advancements, Matt Casters never lost sight of his commitment to open-source principles and community-driven development, ensuring that PDI stayed a flexible and powerful tool for users worldwide.
The Birth of Apache HOP
While PDI continued to evolve, Matt Casters recognized the need for a modern, flexible, and cloud-ready data orchestration platform. The landscape of data integration had changed significantly, with new challenges and opportunities emerging in the era of big data and cloud computing. This realization led to the creation of Apache HOP (Hop Orchestration Platform).
In 2020, Apache HOP was accepted as an incubator project by the Apache Software Foundation, marking a new chapter in its development and community support. This move underscored the project’s commitment to open-source principles and ensured that HOP would receive help from the robust governance and community-driven innovation that the Apache Foundation is known for.
Advantage of Apache HOP compared to Pentaho Data Integration
Apache HOP (Hop Orchestration Platform) and Pentaho Data Integration (PDI)/Kettle are both powerful data integration and orchestration tools. However, Apache HOP has several advantages over PDI, because of its evolution from PDI and adaptation to modern data needs. Below, we explore the key advantages of Apache HOP over Pentaho Data Integration Kettle:
Modern Architecture and Design
Feature | Apache HOP | PDI (Kettle) |
Modular and Extensible Framework | Being more modern it is built as a modular and extensible architecture, allowing for easier customization and addition of new features. Users can add or remove plugins without affecting the core functionality. | While PDI is also extensible, its older architecture can make customization and plugin integration more cumbersome compared to HOP’s more streamlined approach. |
Lightweight and Performance Optimized | Designed to be lightweight and efficient, improving performance, particularly for large-scale and complex workflows | Older codebase may not be as optimized for performance in modern, resource-intensive data environments. |
Hop’s metadata-driven design and extensive plugin library offer greater flexibility for building complex data workflows. Users can also develop custom plugins to extend Hop’s capabilities to meet specific needs.
Enhanced User Interface and Usability
Feature | Apache HOP | PDI (Kettle) |
Modern UI | Features a modern and intuitive user interface, making it easier for users to design, manage, and monitor data workflows. | Although functional, the user interface is dated and may not offer the same level of user experience and ease of use as HOP. |
Improved Workflow Visualization | Provides better visualization tools for workflows and pipelines, helping users understand and debug complex data processes more effectively. | Visualization capabilities are good but can be less intuitive and harder to navigate compared to HOP. |
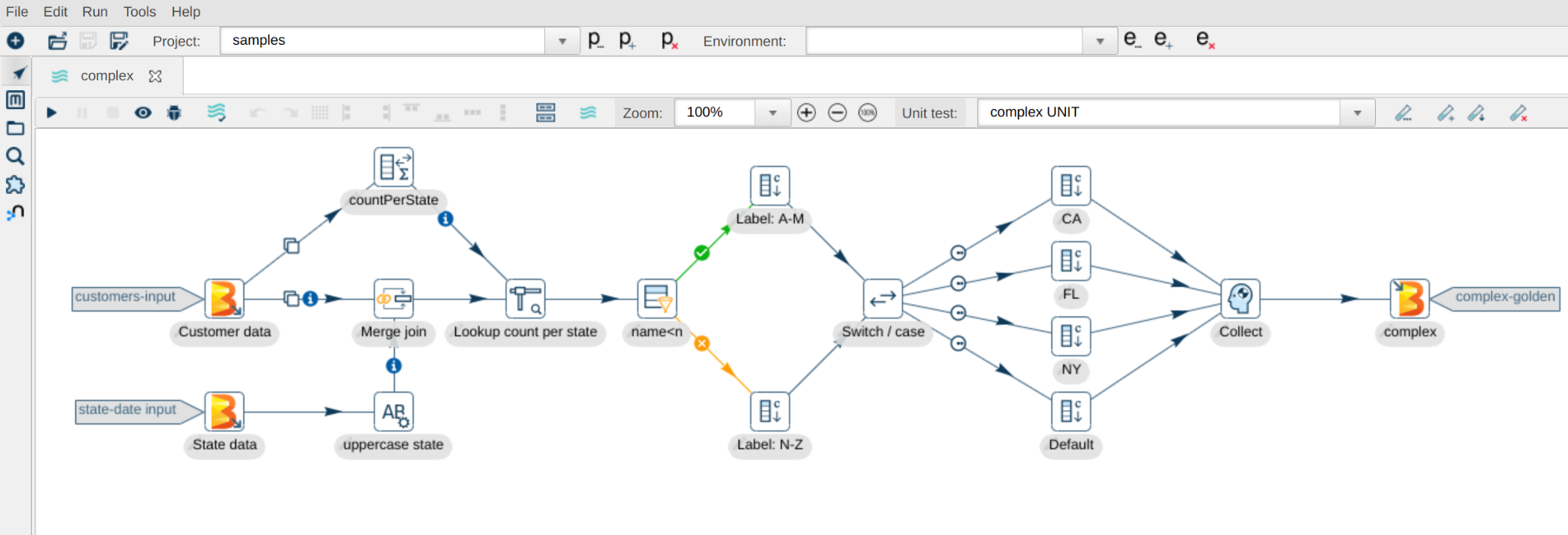
The drag-and-drop functionality, combined with a cleaner and more organized layout, helps users create and manage workflows and pipelines more efficiently.
Apache HOP Web
Apache Hop also supports a Web interface for the development and maintenance of the HOP files unlike Pentaho Data Integration where this feature is still in Beta that too only for the Enterprise Edition. The web interface can be accessed through http://localhost:8080/hop/ui
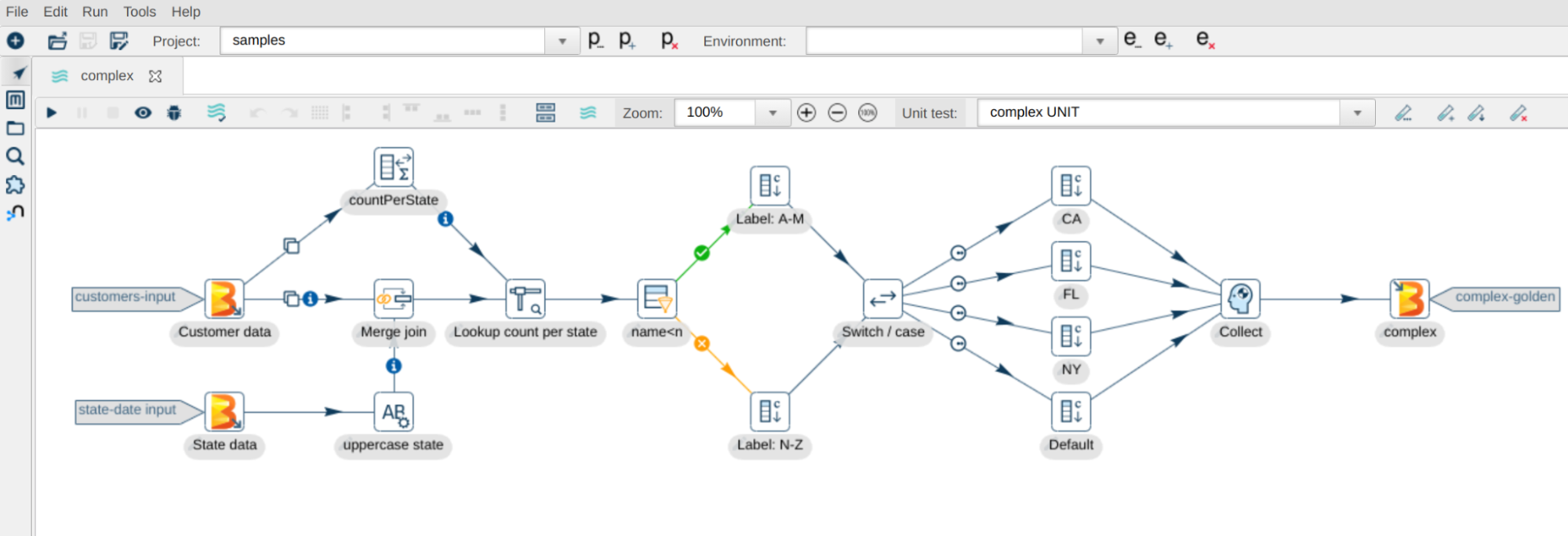
Accessing HOP Status Page: http://localhost:8080/hop/status/
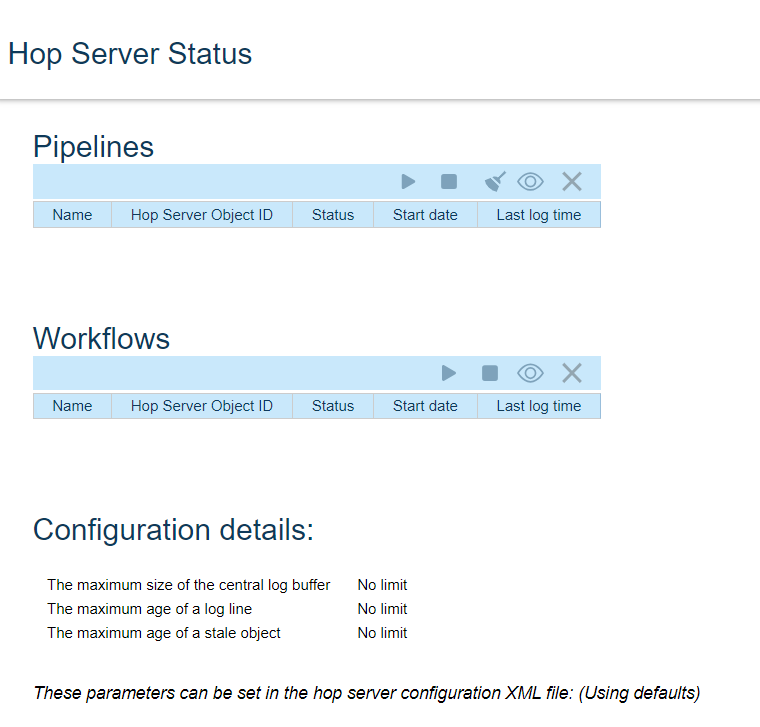
https://hop.apache.org/dev-manual/latest/hopweb/index.html
Advanced Development and Collaboration Features
Feature | Apache HOP | PDI (Kettle) |
Project-Based Approach | Uses a project-based approach, allowing users to organize workflows, configurations, and resources into cohesive projects. This facilitates better version control, collaboration, and project management. | Lacks a project-based organization, which can make managing complex data integration tasks more challenging. |
Integration with Modern DevOps Practices | Designed to integrate seamlessly with modern DevOps tools and practices, including CI/CD pipelines and containerization. | Integration with DevOps tools is possible but not as seamless or integrated as with HOP, especially with the Community edition. |
Apache HOP for CI/CD Integration with GitHub / Gitlab
Apache HOP (Hop Orchestration Platform) is a powerful and flexible data integration and orchestration tool. One of its standout features is its compatibility with modern development practices, including Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. By integrating Apache HOP with GitHub, development teams can streamline their workflows, automate testing and deployment, and ensure consistent quality and performance. In this blog, we’ll explore the advanced features of Apache HOP that support CI/CD integration and provide a guide on setting it up with GitHub.
Why Integrate Apache HOP with CI/CD?
- Automation: Automate repetitive tasks such as testing, building, and deploying HOP projects. 2. Consistency: Ensure that all environments (development, testing, production) are consistent by using automated pipelines. 3. Faster Delivery: Speed up the delivery of updates and new features by automating the deployment process. 4. Quality Assurance: Integrate testing into the pipeline to catch errors and bugs early in the development cycle. 5. Collaboration: Improve team collaboration by using version control and automated workflows.
Advanced Features of Apache HOP for CI/CD
- Project-Based Approach
- Apache HOP’s project-based architecture allows for easy organization and management of workflows, making it ideal for CI/CD pipelines.
- Command-Line Interface (CLI)
- HOP provides a robust CLI that enables automation of workflows and pipelines, easing integration into CI/CD pipelines.
- Integration with Version Control Systems
- Apache HOP supports integration with Git, allowing users to version control their workflows and configurations directly in GitHub.
- Parameterization and Environment Configurations
- HOP allows parameterization of workflows and environment-specific configurations, enabling seamless transitions between development, testing, and production environments.
- Test Framework Integration
- Apache HOP supports integration with various testing frameworks, allowing for automated testing of data workflows as part of the CI/CD pipeline.
Cloud-Native Capabilities
As the world moves towards cloud-first strategies, understanding how Apache HOP integrates with cloud environments is crucial for maximizing its potential. The cloud support for Apache HOP, exploring its benefits, features, and practical applications opens a world of possibilities for organizations looking to perfect their data workflows in the cloud. As cloud adoption continues to grow, using Apache HOP can help organizations stay ahead in the data-driven world
Feature | Apache HOP | PDI (Kettle) |
Cloud Integration | Built with cloud integration in mind, providing robust support for deploying on various cloud platforms and integrating with cloud storage, databases, and services.control, collaboration, and project management. | While PDI can be used in cloud environments, it lacks the inherent cloud-native design and seamless integration capabilities of HOP especially for the Community edition. |
Integration with Cloud Storage
Data workflows often involve large data sets stored in cloud storage solutions. Apache HOP provides out-of-the-box connectors for major cloud storage services:
- Amazon S3: Seamlessly read from and write to Amazon S3 buckets.
- Google Cloud Storage: Integrate with GCS for scalable and secure data storage.
- Azure Blob Storage: Use Azure Blob Storage for efficient data handling.
Cloud-native Databases and Data Warehouses:
Modern data architectures often leverage cloud-native databases and data warehouses. Apache HOP supports integration with:
- Amazon RDS and Redshift: Connect to relational databases and data warehouses on AWS.
- Google Big Query: Integrate with Big Query for fast, SQL-based analytics.
- Azure SQL Database and Synapse Analytics: Use Microsoft’s cloud databases for scalable data solutions.
Cloud-native Data Processing
Apache HOP’s integration capabilities extend to cloud-native data processing services, allowing for powerful and scalable data transformations:
- AWS Glue: Use AWS Glue for serverless ETL jobs.
- Google Dataflow: Integrate with Dataflow for stream and batch data processing.
- Azure Data Factory: Leverage ADF for hybrid data integration.
Security and Compliance
Security is paramount in cloud environments. Apache HOP supports various security protocols and practices to ensure data integrity and compliance:
- Encryption: Support for encrypted data transfers and storage.
- Authentication and Authorization: Integrate with cloud identity services for secure access control.
Compliance: Ensure workflows comply with industry standards and regulations
Features Summary and Comparison
Feature | Kettle | Hop |
Projects and Lifecycle Configuration | No | Yes |
Search Information in projects and configurations | No | Yes |
Configuration management through UI and command line | No | Yes |
Standardized shared metadata | No | Yes |
Pluggable runtime engines | No | Yes |
Advanced GUI features: memory, native zoom | No | Yes |
Metadata Injection | Yes | Yes (most transforms) |
Mapping (sub-transformation/pipeline | Yes | Yes(simplified) |
Web Interface | Web Spoon | Hop Web |
APL 2.0 license compliance | LGPL doubts regarding pentaho-metastore library | Yes |
Pluggable metadata objects | No | Yes |
GUI plugin architecture | XUL based (XML) | Java annotations |
External Link: | https://hop.apache.org/tech-manual/latest/hop-vs-kettle/hop-vs-kettle.html |
Community and Ecosystem
Open-Source Advantages
- Apache HOP: Fully open-source under the Apache License, offering transparency, flexibility, and community-driven enhancements.
- PDI (Kettle): While also open-source and having a large user base with extensive documentation, PDI’s development has slowed, and it has not received as many updates or new features as HOP. PDI’s development was and is more tightly controlled in the recent past by Hitachi Vantara, potentially limiting community contributions and innovation compared to HOP.
Active Development and Community Support
Apache Hop is actively developed and maintained under the Apache Software Foundation, ensuring regular updates, bug fixes, and new features. The community support for Apache HOP is a cornerstone of its success. The Apache Software Foundation (ASF) has always championed the concept of community over code, and Apache HOP is a shining example of this ethos in action.
Why Community Support Matters
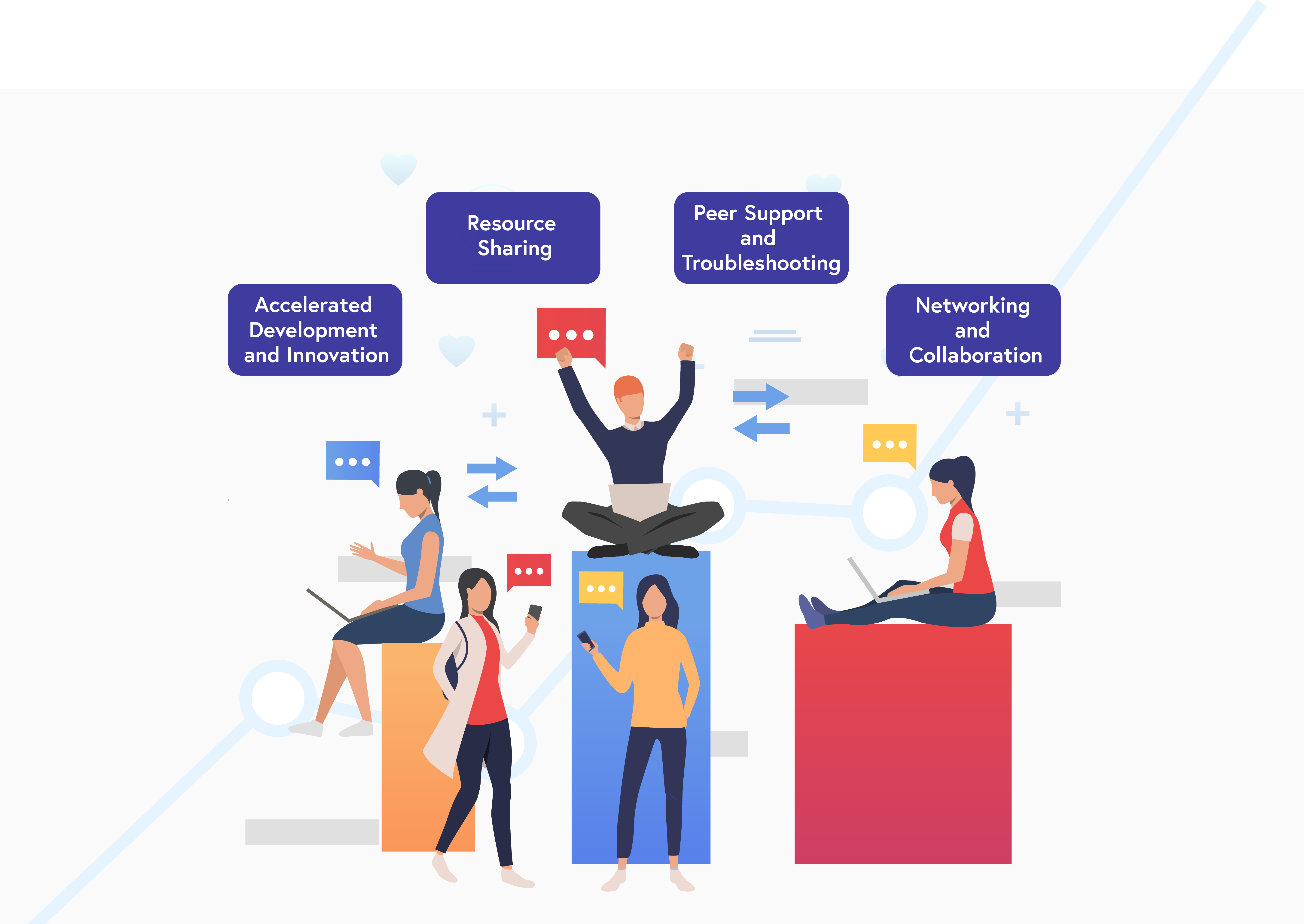
- Accelerated Development and Innovation: The community continuously contributes to the development and enhancement of Apache HOP. From submitting bug reports to developing new features, the community’s input is invaluable. This collaborative effort accelerates the innovation cycle, ensuring that Apache HOP stays innovative and highly functional.
- Resource Sharing: The Apache HOP community is a treasure trove of resources. From comprehensive documentation and how-to guides to video tutorials and webinars, community members create and share a wealth of knowledge. This collective pool of information helps both beginners and experienced users navigate the platform with ease.
- Peer Support and Troubleshooting: One of the standout benefits of community support is the peer-to-peer assistance available through forums, mailing lists, and chat channels. Users can seek help, share solutions, and discuss best practices. This collaborative troubleshooting often leads to quicker resolutions and deeper understanding of the platform.
- Networking and Collaboration: Being part of the Apache HOP community opens doors to networking opportunities. Engaging with other professionals in the field can lead to collaborative projects, job opportunities, and professional growth. It’s a platform for like-minded individuals to connect and create meaningful professional relationships.
All this can be seen from the frequent, consistent releases with key features released in each release captured in the table below.
Version | Release Date | Description |
Apache Hop 3.0 | Q4 2024 | Future Release Items |
Apache Hop 2.10 | August 31, 2024 | Upcoming… The Apache Hop 2.10 release introduced several new features and improvements. Key updates include Enhanced Plugin Management, Bug Fixes and Performance Enhancements, New Tools and Utilities. |
Apache Hop 2.9 | May 24, 2024 | This version includes various new features like static schema metadata type, Crate DB database dialect and bulk loader, and several improvements in transforms. Check out What’s changed. Check here for more details. |
Apache Hop 2.8 | March 13, 2024 | This update brought new AWS transforms (SNS Notify and SQS Reader), many bug fixes, and performance improvements. Check here for more details. |
Apache Hop 2.7 | December 1, 2023 | This release featured the Redshift bulk loader, JDBC driver refactoring, and other enhancements. Check here for more details. |
Apache Hop 2.6 | September 19, 2023 | This version included new Google transforms (Google Analytics 4 and Google Sheets Input/Output), an Apache Beam upgrade, and various bug fixes. Check here for more details. |
Apache Hop 2.5 | July 18, 2023 | This version focused on various bug fixes and new features, including an upgrade to Apache Beam 2.48.0 with support for Apache Spark 3.4, Apache Flink 1.16, and Google Cloud Dataflow. Additional updates included a new Intersystem IRIS database type, JSON input and output improvements, Salesforce input enhancements, an upgrade to Duck DB 0.8, and the addition of Polish language support.Check here for more details. |
Apache Hop 2.4 | March 31, 2023 | This update introduced new features like Duck DB support, a new script transform, and various improvements in existing transforms and documentation |
Apache Hop 2.3 | February 1, 2023 | This release focused mainly on bug fixes and included a few new features. One significant update was the integration of Weblate, a new translation tool that simplifies the contribution of translations. Another key addition was the integration of the Vertica Bulk Loader into the main code base, enhancing data loading speeds to the Vertica analytical database. Check here for more details. |
Apache Hop 2.2 | December 6, 2022 | This release involved significant improvements and fixes, addressing over 160 tickets. Key updates included enhancements to the Hop GUI, such as a new welcome dialog, navigation viewport, data grid toolbars, and a configuration perspective. Additionally, there were upgrades to various components, including Apache Beam and Google Dataflow (Apache Hop) (Apache Issues). For more detailed information, you can visit the Apache Hop 2.2 release page. Check here for more details. |
Apache Hop 2.1 | October 14, 2022 | This release included various new features such as MongoDB integration, Apache Beam execution, and new plugins for data profiling and documentation improvements. Check here for more details. |
Apache Hop 2.0 | June 17, 2022 | Introduced various bug fixes and improvements, including enhancements to the metadata injection functionality and documentation updates. The update also included various new transform plugins such as Apache Avro File Output, Apache Doris Bulk Loader, Drools Rules Accumulator, and Drools Rules Executor, as well as a new Formula transform. Additionally, the user interface for the Dimension Lookup/Update transform was cleaned up and improved. Check here for more details. |
Apache Hop 1.2 | March 7, 2022 | This release included several improvements to Hop GUI, Docker support, Neo4j integration, and Kafka and Avro transforms. It also introduced the Hop Translator tool for easier localization efforts, starting with Chinese translations. Check here for more details. |
Apache Hop 1.1 | January 24, 2022 | Some of the key updates in Apache Hop 1.1 included improvements in metadata injection, enhancements to the graphical user interface, support for more data formats, and various performance optimizations. Check here for more details. |
Apache Hop 1.0 | January 17, 2022 | This version marked Hop’s transition from incubation, featuring clean architecture, support for over 20 plugin types, and a revamped Hop GUI for designing workflows and pipelines. Check here for more details. |
Additional Links: | https://hop.apache.org/categories/Release/ , https://hop.apache.org/docs/roadmap/ |
Few Limitations with HOP
While Apache HOP has several advantages compared to Pentaho ETL, by the nature of it being a comparatively newer platform, there are a few limitations we have encountered when using it. Some of these are already recorded as issues in the HOP Github and are scheduled to be fixed in upcoming releases.
Type | Details |
HOP GUI | The HOP GUI application does not allowto the change “Project Home path” to a valid path after setting an invalid Project Path. |
HOP GUI | Repeatedly Prompting to enter GitHub Credentials |
HOP GUI | While Saving a New Pipeline, HOP GUI Appends the Previously Opened Pipeline Names |
HOP Server | Multiple Hop Server Object IDs for a single HOP Pipeline on the HOP Server |
HOP Server | Hop Server Objects (Pipeline/Workflow) Status is Null and the Metrics Information is not Shown |
HOP Web | Unable to Copy the Transform from one Pipeline to Another Pipeline |
HOP GUI | Log table options in Workflow Properties Tab |
HOP GUI | Showing Folder Icon for HPL Files |
HOP GUI | Dimension Lookup & Update Transform SQL Button Nullpointer Exception |
There are very few issues which can act as an impediment to using Apache HOP depending on the specific use cases. We will talk more about it in the next blog article of this series.
Conclusion
Apache HOP brings a host of advantages over Pentaho Data Integration Kettle, driven by its modern architecture, enhanced usability, advanced development features, cloud-native capabilities, and active community support. These advantages make Apache HOP a compelling choice for organizations looking to streamline their data integration and orchestration processes, especially in today’s cloud-centric and agile development environments. By using Apache HOP, businesses can achieve more efficient, scalable, and manageable data workflows, positioning themselves for success in the data-driven future.
Most importantly, Hitachi Vantara / Pentaho has stopped releasing Community versions of PDI or security patches for nearly 2 years now and also removed the links to download older versions of the software from Source forge too. This makes it risky for users to continue using Pentaho Community Edition in Production due to any non-resolved vulnerabilities.
Need help to migrate your Pentaho Artifacts to Apache HOP? Our experts can help.